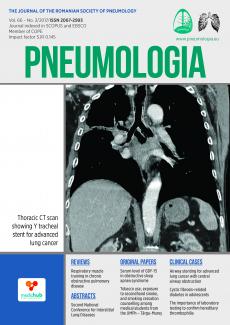
ORIGINAL PAPERS
Diagnostic techniques for organic foreign body aspiration in children – case reports
Mioriţa Toader, Alina Oprea, Corneliu Toader, Andra Beldiman, Olivia Ștefan, Mircea DrăghiciDiagnostic techniques for organic foreign body aspiration in children – case reports
Tracheobronchial foreign body aspiration represents a life-threatening condition especially in young children.
It carries a great amount of mortality and morbidity through the possibility of obstructing the airway and
thus resulting in acute respiratory failure. The diagnostic challenges are brought by the great variability of clinical presentation which sometimes only consists of subtle symptoms. For an optimal therapeutic outcome, only a high index of clinical suspicion can ensure a prompt treatment. The mainstay of both diagnostic and
therapeutic algorithm resides in bronchoscopy. The article reports the multidisciplinary management of two young children with organic foreign body aspiration, outlining the importance of a step-wise diagnostic approach.
Keywords: foreign body, aspiration, pediatric bronchoscopy
Depression in patients with stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a cross-sectional study in the national center for respiratory diseases in Indonesia
Nur Nina Rosrita, Faisal Yunus, Tribowo Tuahta Ginting, Fariz NurwidyaDepression in patients with stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a cross-sectional study in the national center for respiratory diseases in Indonesia Background: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a major cause of morbidity and mortality in the world, including Indonesia. It can cause comorbidities such as osteoporosis, heart failure, diabetes, and depression. Depression is a common comorbidity affecting COPD patients, unfortunately, this comorbidity is often mis- or under-diagnosed.
Objective: The purpose of this study is to reveal the prevalence of depression in stable COPD patients in Persahabatan Hospital Jakarta and its associated factors.
Methods: This is a cross-sectional study in which stable COPD patients who visited COPD Outpatient Clinic in Persahabatan Hospital Jakarta and met the inclusion and exclusion criteria were asked for a history of disease, physical examination, lung function test and underwent Mini International Neuropsychiatric Interview Version (MINI) ICD 10.
Results: One hundred and forty-one patients were enrolled in this study. Prevalence of depression was 19.1%. Subjects with moderate-high COPD assessment test (CAT) score ≥ 10 have 14 times higher risk of having depression (p<0.001) compared to subjects with mild CAT score (< 10). There was a statistically significant association between symptoms-based COPD group (p<0.001),smoking status (p<0.007) and Brinkmann index (p<0.026)with depression. We found no statistically significant association between risk-based COPD group (p=0.799) and airflow limitation (p>1.000) with depression.
Conclusion: The prevalence of depression in stable COPD
patients in Persahabatan Hospital Jakarta was 19.1%.
There was a statistically significant association between
symptoms-based COPD group, smoking status, and Brinkmann index with depression in stable COPD patients.
Keywords: COPD, depression, prevalence, stable
Depression in patients with stable chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: a cross-sectional study in the national center for respiratory diseases in Indonesia
Clinical and laboratory correlations in patients with cystic fibrosis and Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection: the experience of a regional centre
Roxana Smădeanu, Simona Moșescu, Carmen Zăpucioiu, Dumitru OrășeanuClinical and laboratory correlations in patients with cystic fibrosis and Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection: the experience of a regional centre Pseudomonas aeruginosa (Pa) is the most important pathogen affecting the prognosis of patients with cystic fibrosis (CF). Distinguishing the correlations associated with Pa infection may change the way in which investigation and therapeutic plans are approached. This study aims to evaluate the correlations between various factors such as age at diagnosis, nutritional status, homozygous status of delF508 mutation, the number of exacerbations per year, imagistic modifications, the presence of chronic infection with Staphylococcus aureus, serum levels of total immunoglobulins G (IgG) and gammaglobulins and ventilation parameters - forced vital capacity (FVC) and one-second forced expired volume (FEV1) and their association with Pa infection. Methods. The associations between the analyzed parameters have been made by logistic regression; the comparisons between means of continuous variables were performed using Student t-test; the variables distribution was tested using chi-square test, and correlations between variables were assessed using Pearson coefficient. Results. The mean age at the acquisition of Pa was 5.26 (±5.3 years). Of the 50 patients included in the study, 21 acquired the Pa infection having the median age of primo-infection of 3 years. The study identified a greater number of exacerbations per year in those infected with Pa (2.71 compared to 1.38 exacerbations per year; p=0.002); the increase of radiological score with 1 unit associated with an increased risk of infection with Pa (OR 1.31; 95% CI 1.10-1.56; p = 0.002), the mean Brasfield radiologic score is lower for uninfected children (6.9 vs. 11 points, p=0.001); increasing the degree of bronchiectasis associated with Pa infection (OR 3.75; CI 1.77-7.96; p=0.001); gammaglobulin (15.91 vs. 19.42%; p=0.01) or immunoglobulin G values (IgG) (9.8 vs. 11.9 g/L; p=0.05) were higher for those infected.
Conclusions. The increased number of exacerbations per year, the severity of imagistic modifications, and IgG and
gammaglobulins values are associated with Pa infection. Tracking these parameters guides the therapeutic conduct.
Keywords: Pseudomonas aeruginosa, risk factors,
cystic fibrosis




 Diagnostic techniques for organic foreign body aspiration in children – case reports
Diagnostic techniques for organic foreign body aspiration in children – case reports